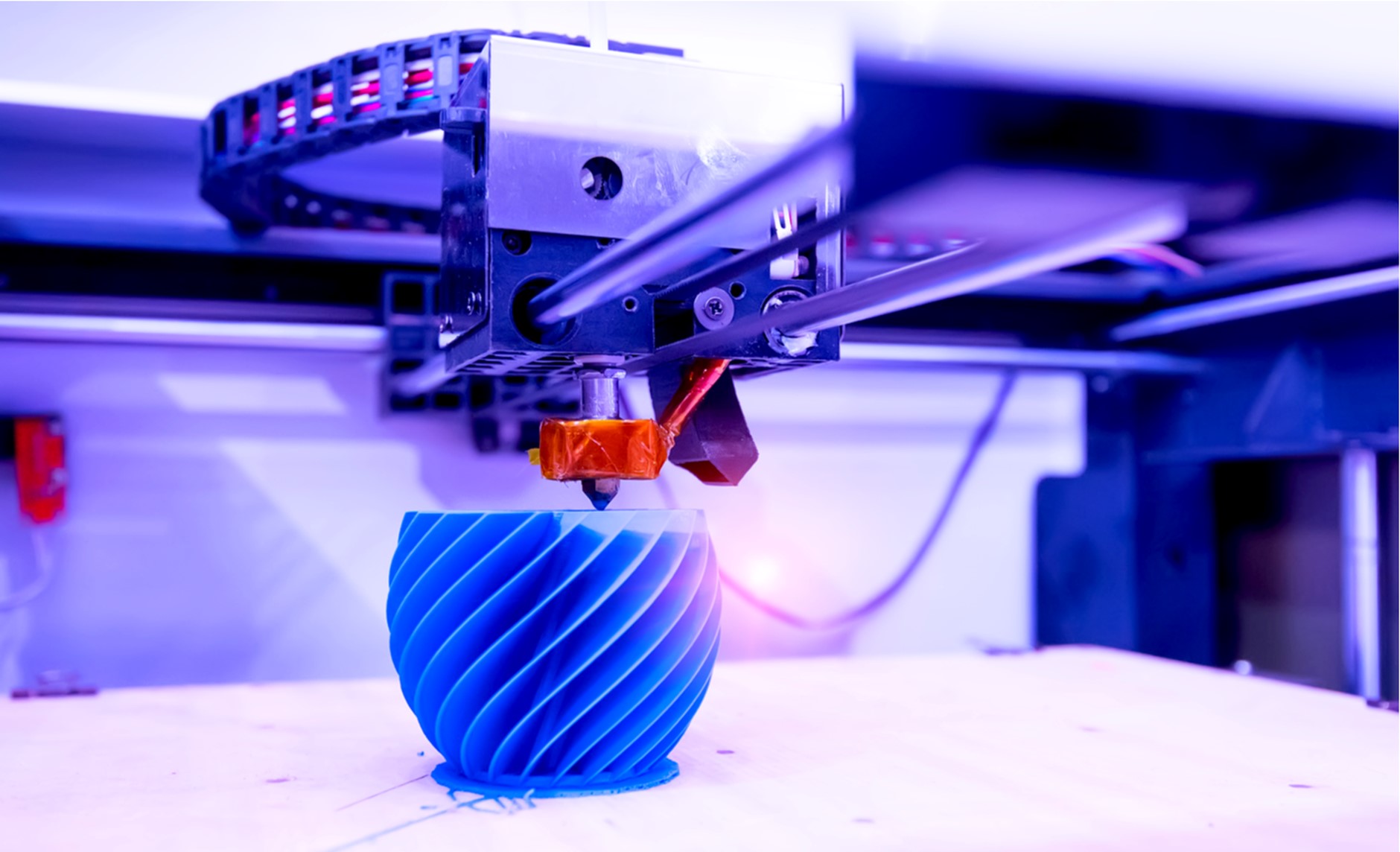
One of the fastest growing and most exciting industries in tech at the moment is certainly found within 3D printing – it is finding success through many different scales from smaller projects like ornaments and figures to much larger full scale model or even full building sizes as Dubai and UAE 3D Printing has really taken off, in the former there are even trials to explore 3D printing entire concrete buildings whilst not yet profitable it is something that is progressing extremely quickly, as Dubai 3D printing in particular looks to be a defining name in the market. But is 3D printing considered a clean technology?
Like most things, it’s not as simple as a yes-or-no answer but there are still plenty of things going in favour of 3D printing on all scales – and when looking at larger scale options like manufacturing and building there is something to be said for printed options. Most manufacturing is a subtractive method – taking a block of raw material and removing the additional parts that aren’t need – this could be cutting wood beams down to size, removing large parts of metal or plastic, or any variation thereof, but 3D printing is different in that it’s an additive manufacturing method – starting with a blank slate, printers build from the ground up and there’s often little to no wasted material and with larger scale options such as a concrete house, it can save greatly on not only energy used, but the material being used and potentially wasted too. As a technology that’s changing and evolving extremely quickly, any potential waste will only look to reduce over time as machines become more efficient and planning options become more streamlined.
With planning in mind too, this is something else that remains on the side of 3D printing and it’s edging towards being a greener option – there is opportunity for some wastage here, getting the right specs and having some trial and error can lead to initial wastage during the design phase but once things have been prepared there’s very little additional work required – plans get loaded into the program and the 3D printing begins and it ensures the same uniform print each time and this is also important when it comes to transporting material too. With energy being used from wherever electricity is generated from, a sustainable energy supply keeps 3D printing neutral in terms of energy usage, and given print plans can simply be sent from one system to another, it can mean manufacturing is done locally if 3D printing is an option too and this once again leads to a greener industry as a whole – as countries around the world expand their 3D printing options and particularly with those already leading with the likes of Dubai 3D printing and UAE 3D printing already being so successful, informed choices can have a net positive impact, particularly as the technology continues to evolve.